SOFIA
20. March 2020
EnMAP
24. March 2020VIRTIS
- Client
- Kayser-Threde GmbH (now OHB)
- Links
- esa VIRTIS
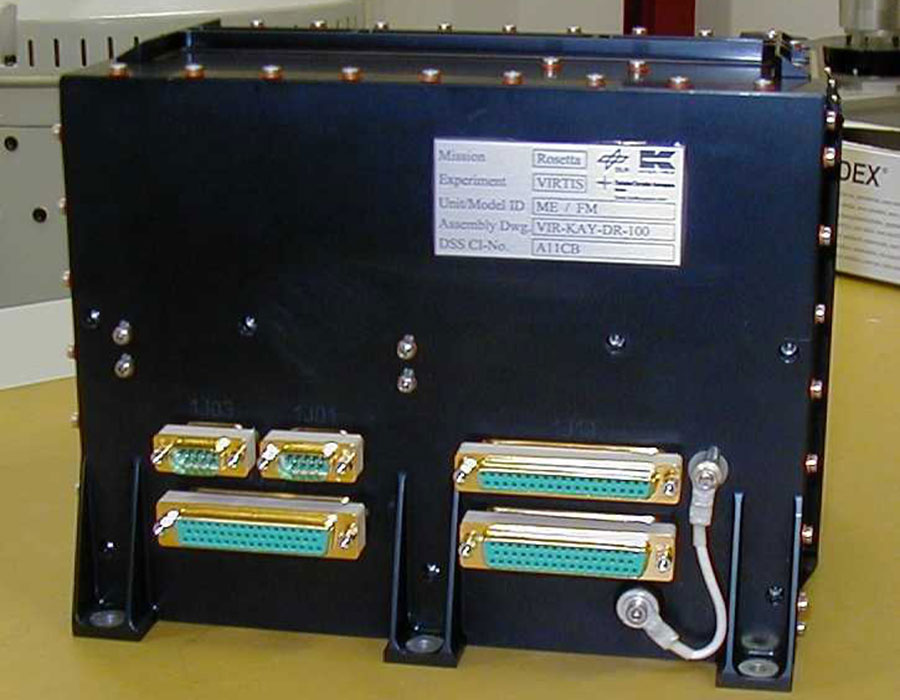
VIRTIS (Visible and Infrared Thermal Imaging Spectrometer)
VIRTIS is a scientific instrument for the analysis of a cometary nucleus or a planet and its environment.
Our contribution
Design: In a subcontract we delivered the mechanical engineering for the Virtis ME (Main Electronic). High demands on the total mass had to be met - especially for space flight conditions.
 Rosetta
Rosetta
One of ESA's "Cornerstone" missions for this century. Origin of name: Stone of Rosetta - deciphering the Egyptian hieroglyphics. Goal: Exploration of comet P/Wirtanen. After the failed launch of the "Ariane 5 Plus" launcher, all further flights were initially cancelled.
Due to the closing of the temporal launch window the replacement comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko was chosen as a new main target. Launch: On March 2, 2004, Rosetta embarked on its incredible 7 billion km journey to the comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko in Ariane 5G flight 158 from Kourou, French Guiana.
In May 2014, Rosetta entered the comet's orbit. On August 6, 2014 it had finished mapping the comet's surface and had found a landing site for the lander Philae to land on the comet.
From then on, Rosetta accompanied the comet until the mission ended on August 13, 2015, the closest point on the comet's journey to the sun.
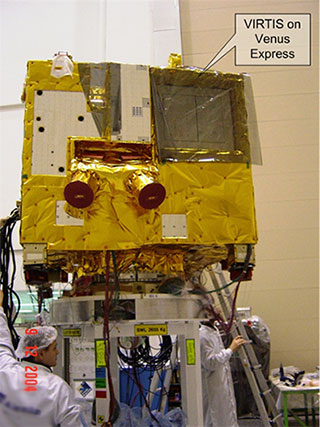
Venus Express
Objective: To explore the structure, chemistry and dynamics of the Venus atmosphere. Launch: On 09.11.2005, the Venus Express set off on its 350 million kilometre journey to our sister planet Venus on board a Soyuz Fregat carrier. The Venus Express mission is scheduled to last at least two Venus days (486 Earth days) and may be extended depending on the condition of the probe.
Aim: To explore the structure, chemistry and dynamics of the Venus atmosphere. Launch: On 09.11.2005, the Venus Express set off on its 350 million kilometre journey to our sister planet Venus on board a Soyuz Fregat carrier. The Venus Express mission is scheduled to last at least two Venus days (486 Earth days) and may be extended depending on the condition of the probe.

